car leasing with insurance – What Are the Costs and How Does it Work?
&
Leasing a car is a more popular option than ever. Leasing is a more affordable option than ownership.
Leasing a car involves paying a small down-payment, usually less than 20% of the car’s value, and then paying monthly fees for leasing the car. At the end of the lease term, you return the vehicle and pay additional fees (such as for mileage overages or repairs to the car).

While the cost of leasing is cheaper than buying or financing a car, it is important to get the insurance aspect correct. Because of the unique quirks of leasing a car such as the fact that you don’t own a car but are responsible for its upkeep and prevention of excessive wear, there are implications for buying insurance.
Read More: Leasing vs. Buying: What’s the difference?
Is coverage mandatory?
As with driving any sort of car, you will be required to have proof of insurance before you drive it off the lot. In most instances, you will not be able to drive a vehicle off the lot before you buy insurance.
If you are leasing a new vehicle after returning your previous vehicle, your insurance will transfer, and you will usually have a limited window within which to inform your insurance company of the change in vehicle details, this can be a period of time from a few days to a few weeks, depending on the state within which you reside.
This may cause an increase in your monthly payment, although it may also result in no additional charges.

Insurance companies don’t factor in whether you own the car or lease it into the cost of your premium since it doesn’t affect whether your risk of a claim. However, your leasing company will most likely have specific requirements when it comes to levels of insurance, particularly in terms of the level of coverage and the deductibles.
Why is higher coverage required?

Because you do not own the car, the leasing company wants to take extra steps to protect their asset.
This means that they will require you to have higher levels of insurance, or an increased type of coverage. In effect, they are guaranteeing that you will carry the appropriate coverage requirements to protect the car from damage.
Again, before they let you drive off the lot, they will require you to provide proof of certain levels of insurance coverage. You will also need to list the leasing company as an additional interest and loss payee (meaning that they will get the payout for any damages to the vehicle).
What are the three most common requirements for insurance?
- Higher liability
- Collision and comprehensive coverage
- Lower deductibles
What are higher liability limits?
In most states the basic form of liability insurance takes two main forms:

Bodily Injury Liability:
This covers injuries other than your own. The typical minimum level is $25,000 per person and $50,000 per accident (although it does vary from state to state).

Property Injury Liability:
This pays for damage to property and is usually set at a minimal $10,000 per accident

Most (but not all) leasing companies will require liability coverage beyond this. For example, Mercedes-Benz and Kia both require Bodily Injury Liability to be $100,000 per person and $300,000 per accident as part of their lease. They also require $50,000 per accident in property damage.
These are fairly typical of lease agreements. Some may also require additional coverage such as uninsured/underinsured motorist and personal injury protection coverage, which can vary by state. You should check insurance requirements prior to signing the lease agreement.
What are collision and comprehensive insurance policies?
One of the most common insurance requirements when it comes to leasing a car is the requirement for additional insurance beyond liability coverage.
Since the lessor retains ownership of the car, they require reassurance that the car will be repaired in the event it is damaged.
They will usually require the following:

Collision coverage:
This will pay for repairs to the insured car in the event of a collision (liability insurance only covers damage to another vehicle. If you’re at fault, your vehicle repairs will not be covered by insurance unless you carry collision coverage). Collision coverage is a requirement for leased vehicles.

Comprehensive coverage:
This covers repairs to your car for damages not caused by a collision (i.e. after natural disasters or non-crash-related damage). It also covers you in the event your vehicle is stolen.
What about a lower deductible?
Your leasing company may also set an upper limit on your deductible.
A deductible is an amount you will need to pay out of pocket before the insurance company will contribute. An insurance company will lower your monthly premiums if you have a higher deductible, although you will increase your own financial exposure.
As a result, leasing companies set an upper limit as an added reassurance that the leased vehicle will be repaired in the event it is damaged.

Most leasing companies require that the upper limit for a deductible be $1,000, or $500 in some cases. This means that your monthly premiums may be higher than if you owned the vehicle directly.
Can you bundle with your lease payments?
In some instances you can actually buy your insurance from the lessor, meaning your can bundle everything together instead of maintaining separate auto insurance policies and lower your monthly payments.
These services are becoming more and more common, with ‘auto subscription’ services bundling everything together. Canvas, a subsidiary of Ford is one of the pioneers of this type of service.
Prices vary based on the type of vehicle and package selected but may include maintenance, insurance, mileage fees, or other fees. Still, this is a great option for those who are leasing a car and looking for cheap auto insurance.

Bundling these together can be a great way to save money, and save you the hassle of car ownership. This is an innovative option for car purchasing or leasing options, as drivers seek more modular forms of ownership, which may allow less of a commitment.
Can you only use original equipment manufacturer parts?

One of the downsides of leasing a car is that the lease will often require that you use Original Equipment Manufacturer Parts (OEM).
This is a disadvantage of leasing, because that the leasing company gets to choose the repairs, and you have to pay for them. As a result, if you lease a car, particularly if it is a luxury car, your insurance may increase.
If you purchase Mechanical Breakdown Insurance (see below) you may have more flexibility on where you get your car repaired; however, getting repairs can be expensive with a leased car because of the specific requirements stipulated by the terms of the lease.
What is gap insurance?

Gap insurance is useful for financed or leased vehicles because of depreciation. Cars begin to lose value the second you drive them off the lot, with most vehicles losing around 20% of their value in the first year.
If you total or badly damage your car (or in some instances when it is stolen) the insurance will pay for
the market value of the car, which may be less than the amount you owe. In this instance, gap insurance covers the difference between the two.
Gap insurance may be compulsory with a lease, but if not, it still may be a good idea:
-
If you paid a down payment of less than 20% of the vehicle’s total cost (at the time of sale)
-
If you have a contract of five years or longer
-
If you purchased or leased a vehicle that depreciates faster than the average
-
Rolled over negative equity from a previous lease or loan into the new loan
If any of these circumstances apply to you, then gap insurance is a solid option to cover you in the event of a catastrophic crash or car theft.
What other types of insurances are there?
As well as gap insurance, you may be able to purchase other insurance types that will cover you financially during the term of your lease (and at lease end). Each of the following options covers some of the most common issues when it comes to leasing a car, to avoid getting stung with out-of-pocket overages at the end of your lease.
Wear and Tear Insurance:

Wear and tear on a car is an inevitable part of driving. The small dings that you get from driving, whether it be chipped paint or tiny scratches, are your financial responsibility according to the leasing company. When your lease ends, you have two options:
- Pay a fee to the leasing company to do the work (this usually includes a markup)
- Pay to have the car repaired to an as-new standard
The five most common items that are typically charged as wear and tear, and the cost of replacements are:
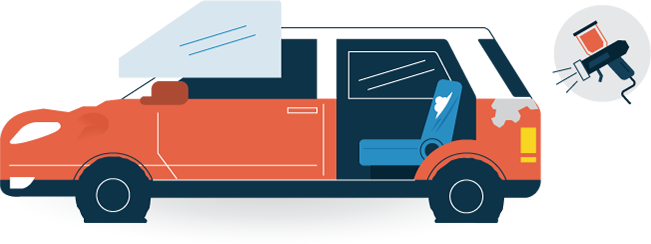
- Exterior Dings and Dents$45-$135 per ding
- Tears and Burns to Upholstery$35-150 (depending on upholstery type)
- Tires$75-200 for replacement tires
- GlassAnywhere from $25 to replace a chip to $200 for replacing a windshield
- Paintwork$35-70
These fees can add up, especially if you have to replace worn tires, or have small amounts of damage to a critical part of the vehicle. Wear and Tear Insurance will cover you in the instance that you have significant costs from repairing the wear and tear.
Is there mechanical breakdown insurance?

Mechanical breakdown coverage pays for car repairs that are not included in a car’s warranty. This doesn’t include damage caused by accidents, which are covered under collision or comprehensive insurance. Your car dealership will usually offer you an extended warranty.
In those circumstances, mechanical breakdown insurance may be a better option, because:
- It will cover more parts of the car
- It will cost less (because you can shop around rather than buy from a dealer)
- It will give you a choice of mechanics to use if something goes wrong (rather than requiring you to go through a dealer)
- You can bundle it with your other insurances to save money
The most common things covered by a basic mechanical breakdown insurance policy are:
- Engine parts
- Drivetrain
- Transmission
- Exhaust
- Brakes
- Alternator and other electrical components
More advanced policies may also cover the following:
- Steering
- Air conditioning/ heating
- Fuel system
How Does a Warranty Cover Your Car?

In most cases, the warranty on your car functions as a form of insurance policy, in that it protects you if something fundamental breaks, since the cost of repair will be borne by the manufacturer. The standard coverage from a warranty is 36,000 miles and three years. If anything breaks within this period, you can return the car to the dealer, and they will pay for the cost of repairs.

Warranties also cover the powertrain, which means that your engine and transmission are covered. This is critical because typically these are the most expensive parts of the car to repair. Warranties are mandated by federal law to provide an 8 year or 80,000-mile warranty for the catalytic converter and other emission controls.

Something that’s also worth examining is whether roadside assistance is covered in your warranty.
This is becoming a more common feature of warranties, where once it was the preserve only of luxury brands. You should make a point to closely check your warranty at the point of leasing a car, and making a list of what is covered.

Leasing a car is an increasingly popular way of financing a vehicle. It is often cheaper than taking out an auto loan and allows you to have a new car at an affordable rate. For today’s adults, many of whom are experiencing a higher cost of living than their elders, leasing is a great way to access a vehicle. However, knowing how to manage the insurance aspects of it is critical, since it can save money if done correctly, but if handled incorrectly could cost money. Being savvy with your insurance is as important as getting a great deal on the car.
Read more: How to Manage Your Auto Insurance Policy






